MongoDB vs Redis: a Complete Comparison in 2025

Explore the strengths of Redis and MongoDB in 2025.
| Features | Redis | MongoDB |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Key/value store with in-memory access | Document-oriented with flexible schema |
| Scalability | Manual shard management | Built-in sharding for horizontal scaling |
| Storage | In-memory storage limited by RAM | On-disk storage for large datasets |
| Speed | Faster due to in-memory access | High speed with on-disk data |
| Data Types | Various data structures, RAM-limited | Hierarchical and nested data supported |
| Use Cases | Caching, real-time analytics | Big data applications, content management |
| Latency | Sub-millisecond | Higher than Redis |
| Throughput | High | Moderate |
| Real-time Processing | Excellent | Not optimal |
If you need fast speed for real-time analytics or caching, Redis is the top choice in 2025. MongoDB is ideal if you want more flexibility for big data or content management. Many experts agree that both Redis and MongoDB NoSQL solutions can scale effectively, but each excels in different areas. For instance, MongoDB supports companies like Uber, while Redis powers platforms such as Twitter. The table below highlights the strengths of each NoSQL database:
| Database | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|
| MongoDB | Big data applications, content management, IoT projects |
| Redis | Caching, real-time analytics, message brokering |
When deciding between Redis and MongoDB NoSQL databases, consider factors like performance, scalability, data models, and pricing. Evaluating these aspects will help you select the best solution for your specific needs.
It is important to know how MongoDB and Redis work before picking one. Both are well-known NoSQL databases. They are strong in different ways. MongoDB uses a document model. You save data as documents that can change shape. Redis is an in-memory key-value store. It is very fast because it keeps data in memory.
Here is a table that shows the main differences between MongoDB and Redis:
| Feature | MongoDB | Redis |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Document-oriented with flexible schema | Key/value store with in-memory access |
| Scalability | Built-in sharding for horizontal scaling | Manual shard management |
| Storage | On-disk storage for large datasets | In-memory storage limited by RAM |
| Speed | High speed with on-disk data | Faster due to in-memory access |
| Data Types | Hierarchical and nested data supported | Various data structures, RAM-limited |
MongoDB lets you use many types of data models. You can store complex data and grow your system easily. Redis is great for speed and quick answers. It gives you very fast response times because it uses memory.
When you check performance in 2025, Redis is best for reading lots of data. It keeps CPU use low, even with many users. MongoDB uses more CPU but works well with big data sets. Redis needs more memory, so you must have enough RAM for large jobs. MongoDB saves data on disk, so you can keep more information.
Pick MongoDB or Redis based on what your project needs. Here are the best times to use each one:
MongoDB:
You want to handle big data or lots of content.
You need flexible data models for IoT or analytics.
You work with data that has layers or is nested.
You want to grow your system easily with built-in sharding.
Redis:
You need real-time analytics or caching.
You build chatbots, AI agent memory, or message brokering.
You want high speed and quick answers.
You need very fast response times for your app.
Here is a table that shows which database is better for high-speed, low-delay apps:
| Feature | Redis | MongoDB |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage Type | In-memory | Disk-based |
| Latency | Sub-millisecond | Higher than Redis |
| Throughput | High | Moderate |
| Real-time Processing | Excellent | Not optimal |
| Use Cases | Real-time apps | Flexible data models |
Tip: If you want both speed and flexibility, use Redis and MongoDB together. Redis can cache data and do real-time jobs. MongoDB can store and organize complex data for your app.
The choice depends on what you need. If you want fast speed for real-time jobs, Redis is best. If you need to work with big data and flexible models, MongoDB is better. The redis mongodb nosql debate in 2025 is about these strengths. Pick the database that fits your work and business needs.
MongoDB is a database that saves data on disk. It uses a flexible document model. You can keep data as JSON-like documents. Each document can look different from the others. This helps you store many types of information. MongoDB lets you search and filter your data fast.
MongoDB has a client app, a query engine, and a storage engine. The storage engine puts your data on disk. You can save lots of data without worrying about memory. MongoDB also has sharding and replication. These help you grow your system and keep data safe.
New updates make MongoDB faster. In version 8.0, reads are 32% quicker. Updates are 59% faster. Time-series queries are over 200% faster. These changes help you work with big data and analytics better.
Redis works in a different way. It is an in-memory key-value store. Data is kept in memory, so it is very fast. You get answers in less than a millisecond. Redis supports many data structures like strings, lists, sets, hashes, and sorted sets. This makes Redis good for real-time apps.
Here is a table that shows the main parts of Redis:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Client Application | Talks to Redis using a client library. |
| Command Parser | Reads commands from the client. |
| Command Executor | Runs commands and handles data structures. |
| Data Structures | Strings, lists, sets, hashes, sorted sets. |
| Persistence | Keeps data safe after restarts. |
| Storage Engine | Uses both memory and disk to store data. |
| Memory | Holds in-memory data for quick access. |
| Disk | Gives storage that stays after shutdown. |
Redis keeps getting better. Redis Data Integration 1.12 now works with MongoDB and Atlas. You can sync and cache MongoDB data in Redis. Redis Insight 2.70 lets you tag database connections. This makes it easier to find and use your databases. New APIs help you find source database info and check transformation jobs.
When you look at redis mongodb nosql solutions, MongoDB gives you flexibility and strong analytics. Redis gives you speed and real-time performance. Both are top nosql databases in 2025.

Image Source: unsplash
MongoDB lets you save data as documents. These documents look like JSON files. Each one can have its own shape. You can put arrays and nested data inside. This helps you keep complex info neat. MongoDB is good for big data and content jobs. You can grow your database with sharding and replication. These features help keep your data safe.
MongoDB puts data on disk. You do not need to worry about running out of memory. You can work with huge datasets. On Linux, MongoDB can hold up to 128 terabytes if you skip journaling. Windows can also reach 128 terabytes. The chart below shows how much data you can store on different systems.
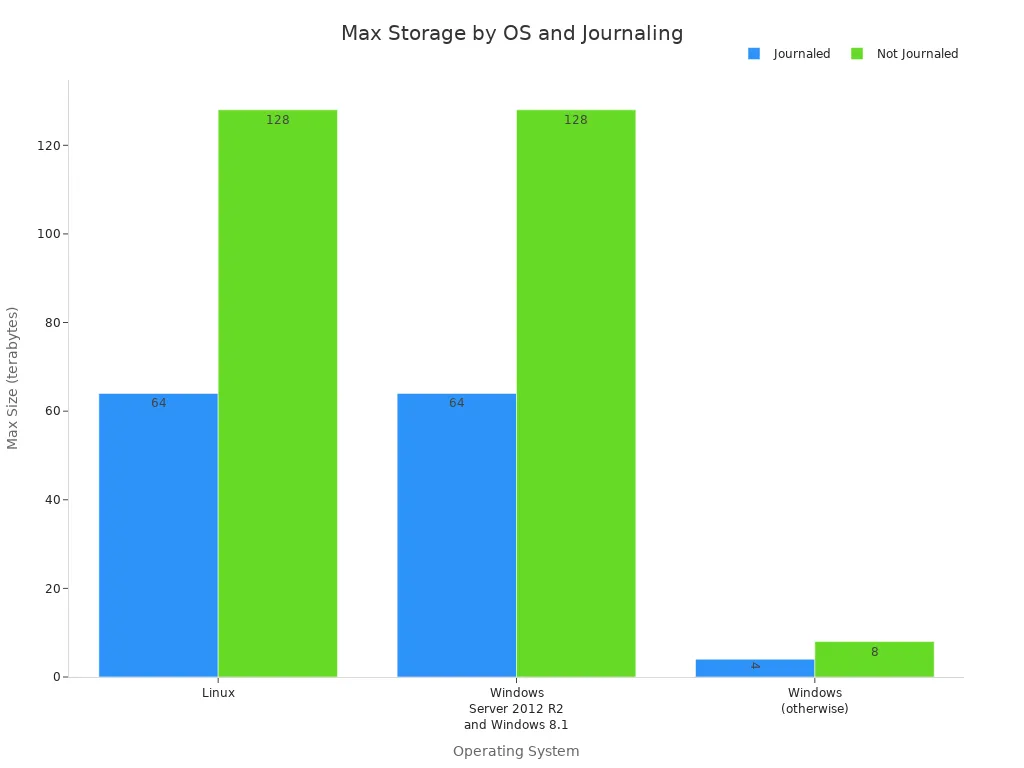
MongoDB uses smart caching. You can use data that is bigger than your server’s memory. This makes MongoDB a good pick for apps needing flexible schemas and lots of space.
Redis keeps all your data in RAM. This makes it super fast. You can use Redis for real-time analytics and caching. It also works for message brokering. You get answers in less than a millisecond.
Redis lets you use many data types. You can use strings, lists, sets, and hashes. Sorted sets are also supported. Redis is great for apps that need speed. You need enough RAM for your data. If your data grows, you must add more memory.
Here is a table that compares MongoDB and Redis data storage:
| Feature | MongoDB | Redis |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Document-oriented (BSON) | In-memory key-value store |
| Data Structure | Flexible, supports nested data and arrays | Various structures (strings, lists, sets) |
| Storage Efficiency | Optimized for large volumes and semi-structured data | Primarily in-memory, fast access times |
| Persistence | Supports disk storage with sharding and replication | Snapshotting and append-only file options |
| Use Case | Applications needing flexible schema and scalability | Performance-critical applications |
When you look at redis mongodb nosql solutions, MongoDB is best for flexible and growing storage. Redis is best for speed and quick data access.

Image Source: pexels
When you look at speed, MongoDB and Redis are different. Redis is an in-memory database. It keeps all data in RAM. This makes Redis super fast. You get answers in less than a millisecond. Redis works well for session caching and leaderboards. It is also good for job queues. These jobs need quick replies and lots of data moving fast.
MongoDB saves data on disk. It is still fast with big datasets. MongoDB has built-in caching to help speed up searches. You can use rich queries and indexing to find data quickly. MongoDB handles big data and complex documents well. If you want flexible data models and easy growth, MongoDB is a good pick.
Here is a table that shows how each database works in real-time:
| Database | Strengths | Use Cases | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | Schema-less design for flexibility | E-commerce sites for personalized recommendations | May require optimization for write-heavy workloads |
| Rich querying and indexing | Social media platforms | ||
| Horizontal scalability | |||
| Redis | In-memory storage for unmatched speed | Online gaming platforms for real-time rankings | Best suited for temporary data storage |
| Supports various data types | Session management | Requires additional configuration for persistence | |
| Pub/Sub messaging for real-time notifications |
You want your app to be fast when users need quick results. Redis is great for real-time jobs. You can use it for pub/sub messaging and session management. Redis is also good for caching. These features help online games, chat apps, and AI agent memory. Redis gives updates in less than a millisecond.
MongoDB can do real-time analytics too. You can use it for e-commerce and social media feeds. MongoDB lets you change data shapes easily. You can grow your database as your app gets bigger.
Here are some common ways to use them:
Use MongoDB for apps that need flexible data, like e-commerce and social media.
Use Redis for fast jobs like session caching, leaderboards, and pub/sub messaging.
When you compare redis mongodb nosql solutions, Redis is best for speed and real-time work. MongoDB is best for flexible data and analytics. You can use both together for fast caching and big storage.
You want your database to get bigger as your data grows. Both MongoDB and Redis can split data across many servers. This is called sharding. MongoDB uses range-based sharding. You can choose how data spreads out. This helps you balance your work better. Redis uses hash-based sharding. Redis Cluster splits keys into 16,384 slots. Each slot goes to a different server. This way, you can manage data well. If a server fails, the system stays strong.
Here is a table that shows how sharding works in MongoDB and Redis:
| Feature | MongoDB Sharding | Redis Sharding |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Range-based | Hash-based |
| Control | Granular data distribution | Automatic slot assignment |
| Scalability | High, with flexible growth | High, with efficient partition |
| Fault Tolerance | Built-in | Automatic failover |
Sharding helps both databases handle more users and bigger data. This makes MongoDB and Redis good for nosql scalability.
Replication keeps your data safe and easy to get. MongoDB uses replica sets. There is one main server and other backup servers. If the main server stops, a backup takes over. This keeps your data safe and your app running. Redis uses replication and clustering. You can copy data from one server to others. Redis Cluster can switch servers if one fails. This means you get quick recovery and less downtime.
Here are some good things about replication in both databases:
Your data stays safe if hardware breaks.
Your apps work more often without stopping.
You can read data from many servers, which helps you scale.
Tip: Use sharding and replication together. Your system will grow and stay reliable.
You want your database to work all the time. If something breaks, it should keep going. MongoDB and Redis are built for high uptime. They use groups of servers that help each other. If one server stops, another one steps in. This keeps your app running without stopping.
MongoDB uses replica sets to stay online. A replica set has one main node and backup nodes. If the main node fails, a backup takes over fast. You will not notice much downtime. MongoDB also has automatic failover and load balancing. These features help keep your data safe and easy to get.
Redis uses a leader-follower setup. The leader writes data. The followers read data. If a follower loses connection, it tries to reconnect. Redis first tries a quick resync. If that does not work, it does a full resync with data snapshots. This keeps your data correct and your service working.
Note: High availability means your app works even if a server fails. MongoDB and Redis use extra servers and smart networks to make this happen.
Here is a chart that shows how bad recent security problems were for both databases. Security matters for uptime because problems can cause outages.

Failover helps your database keep working if a server fails. MongoDB and Redis both have strong failover systems.
MongoDB:
Uses replica sets for automatic failover.
If the main node fails, a backup becomes the new main.
The switch is quick, so your app stays online.
Redis:
Uses leader-follower replication.
Followers try to reconnect and resync if the leader fails.
If needed, a follower can become the new leader.
Both databases handle failover with little downtime. You get a reliable service and less worry. When you look at MongoDB and Redis, both give strong high availability. They use different ways to do this. Both are good for important apps that must stay online.
When you choose a database, you need to know how much it costs and what license it uses. MongoDB and Redis offer different licensing models and price points. You can see the main differences in the table below:
| Database | Pricing | Licensing Options |
|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | Free tier; paid plans from $57/month | Server Side Public License (SSPL); Atlas is SaaS |
| Redis | From $7/month (cloud); enterprise quote for self-hosted | RSAL, Redis Source Available |
MongoDB gives you a free tier. You can start without paying. If you need more features or support, you can choose a paid plan. Paid plans start at $57 per month. MongoDB uses the Server Side Public License (SSPL). This license lets you use MongoDB for free, but you must follow some rules if you offer MongoDB as a service.
Redis also has flexible pricing. You can use Redis in the cloud starting at $7 per month. If you want to run Redis on your own servers, you can get an enterprise license. Redis uses the Redis Source Available License (RSAL). This license lets you use Redis for most projects. You need a special agreement for some commercial uses.
Note: Always check the license terms before you pick a database for your business.
Both MongoDB and Redis give you strong cloud options. You can run MongoDB Atlas as a fully managed service. Atlas works on AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. You can scale your database up or down with a few clicks. You get backups, monitoring, and security built in.
Redis offers managed cloud services too. You can use Redis Cloud on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Redis Cloud gives you high speed, automatic scaling, and built-in security. You can also use Redis on your own servers or in a hybrid setup.
If you want easy setup and less work, cloud options help you start fast. You can focus on building your app while the service handles the database for you.
Pick MongoDB if your project needs flexible data models. It is good for handling big and complex data. MongoDB works well for AI, analytics, and business apps. Here are some times when MongoDB is the best choice:
You want to build AI apps fast. MongoDB supports tools like MAAP. These tools help groups make smart solutions.
You need to connect with top AI tech. MongoDB works with leading platforms. This makes your system stronger.
You want to lower risks when adding AI. MongoDB helps you avoid common problems.
Pick Redis if your project needs speed and real-time data. Redis is great for caching and session management. It is also good for apps that need instant results. Here are some common ways to use Redis:
Caching is the main reason to use Redis. You can keep often-used data in memory. This makes your app faster and cuts down on wait times.
Redis is good for session management. You can keep user sessions active in web apps.
Real-time processing is easy with Redis. You can use it for leaderboards, analytics, and streams.
Redis has TTL features. You can set keys to expire. This helps with rate limits and session control.
You can use MongoDB and Redis at the same time. This gives you both speed and flexible data. Here are some ways to use both:
Redis is a fast cache. It helps you get data quickly.
MongoDB keeps data for a long time and for deep analysis.
In shopping or games, Redis handles real-time data. MongoDB does the analytics.
In health or money apps, Redis gives quick access to key data. MongoDB stores big sets of data.
Tip: Using MongoDB and Redis together helps you get fast results and store lots of data. This mix works well for many types of businesses.
MongoDB has changed a lot since it began. It started in 2007. In 2009, the team made it open source. Over time, MongoDB got many new features. These features help people work with data more easily. The table below shows what was added in each big version:
| Year | Version | Major Features Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2.2 | Aggregation pipeline |
| 2013 | 2.4 | Text search, Google V8 JS engine, MongoDB Enterprise |
| 2015 | 3.0 | WiredTiger storage engine, pluggable storage engine API, increased replica set member limit |
| 2017 | 3.6 | Multi-collection joins, change streams, JSON Schema support |
| 2018 | 4.0 | Transactions across multiple documents |
| 2019 | 4.2 | Distributed transaction support |
| 2020 | 4.4 | Union aggregation, refinable shard keys, hedged reads |
MongoDB got faster for many uses. You can run queries quicker and write lots of data at once. New updates made time series data much faster, over 200% better. You can see how MongoDB improved in the chart below:
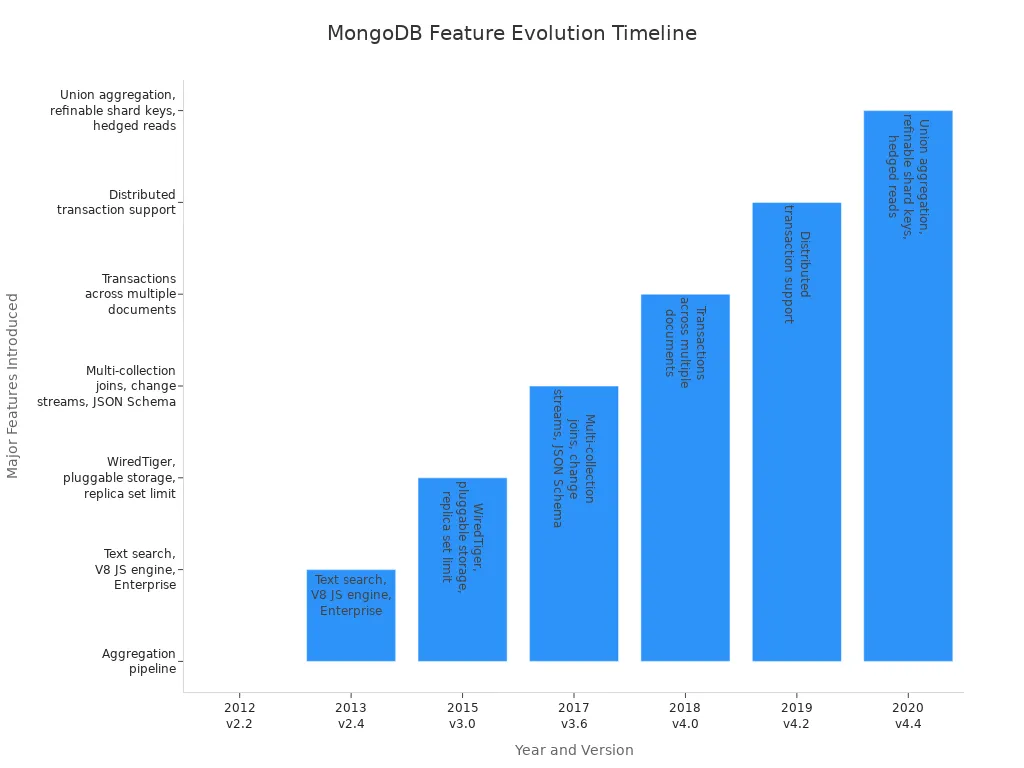
MongoDB’s flexible document model helps with big data and AI. It is a top pick for these kinds of projects.
Redis began in 2009. It focused on being fast and simple. Redis keeps getting better to help with new needs. Many features were added to make apps faster and more reliable. The table below lists some important updates:
| Version | Major Updates and Features Introduced |
|---|---|
| 6.0 | Introduction of Access Control Lists (ACL) for improved security. |
| 6.2 | Enhanced control over Pub/Sub channel names in ACL. |
| 7.0 | Introduction of ACLv2 for granular permission control and promotion of subcommands to first-class citizens. |
Redis hit big milestones to help you scale and protect your data:
2010: Redis 1.0 came out with basic data types and saving.
2013: Redis Sentinel added high availability and failover.
2015: Redis Cluster let you split data across servers.
2018: Modules API let you add custom data types and commands.
2024: Redis Stack added search, JSON, time series, and graph features.
You can trust Redis for real-time analytics, caching, and AI agent memory. Redis keeps getting faster, safer, and more flexible as it grows.
MongoDB and Redis are both good for different things. Look at the table below to see a quick summary:
| Feature | MongoDB | Redis |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Flexible schema, strong queries, sharding | Sub-millisecond speed, versatile data |
| Best For | Content, analytics, user data | Caching, real-time, session storage |
Here is how you can pick the best database in 2025:
Think about what your project needs and how much money you have.
See which database matches your needs the best.
Look at open-source choices if you want to save money.
Keep in mind, the best database is the one that works for your project and fits your budget.
MongoDB lets you store documents in a flexible way. Redis is used when you want very fast data access. MongoDB is good for handling big and complex data. Redis is best when you need quick speed and caching.
Redis is the best choice for real-time analytics. It gives answers in less than a millisecond. Redis works better than MongoDB for live dashboards and fast data.
You can use both at the same time. MongoDB stores your complex data. Redis helps by caching and making frequent searches faster. Using both gives you speed and flexibility.
Redis is great for AI agent memory and fast vector searches. MongoDB is used to keep large, organized datasets and training data. Many AI projects use both to get the best results.
MongoDB uses sharding and replica sets to grow easily. Redis uses clustering and partitioning for strong performance. Both let your system get bigger as your data and users grow.
SQLFlash is your AI-powered SQL Optimization Partner.
Based on AI models, we accurately identify SQL performance bottlenecks and optimize query performance, freeing you from the cumbersome SQL tuning process so you can fully focus on developing and implementing business logic.
Join us and experience the power of SQLFlash today!.