AI-DQL Optimization: From Experience to Intelligence


In today’s data-driven applications, SQL performance directly impacts user experience, system stability, and resource efficiency. Traditional SQL optimization has long been a core challenge for database administrators (DBAs) and developers, often relying on manual experience, heuristic rules, and extensive performance testing, which is inefficient and struggles with complex, dynamic business scenarios.
With the rapid advancement of AI technology, particularly large language models (LLMs), we’re entering a new era of AI-powered SQL optimization. AI can now understand SQL intent, analyze data distribution, evaluate indexing strategies, and make optimization decisions considering business context, much like an experienced DBA.
Rule Rigidity: Traditional SQL optimizers depend on static rule sets, making them inflexible when encountering new SQL patterns or business requirements. Each new pattern requires adding new optimization rules, leading to an exponentially growing rule set that becomes increasingly difficult to maintain.
Database Differences: Different databases have varying SQL syntax and optimization strategies. Transferring optimization rules across databases often requires complete rewriting, making cross-database optimization costly.
Lack of Business Understanding: Traditional SQL optimizers typically focus only on the SQL statement itself, lacking understanding of the business logic behind it, making it difficult to make globally optimal optimization decisions.
AI can learn from vast amounts of SQL statements and business knowledge to understand the intent behind SQL queries. It can infer table sizes and field contents, providing more accurate optimization basis. For example:
| |
| |
Using AI for optimization:
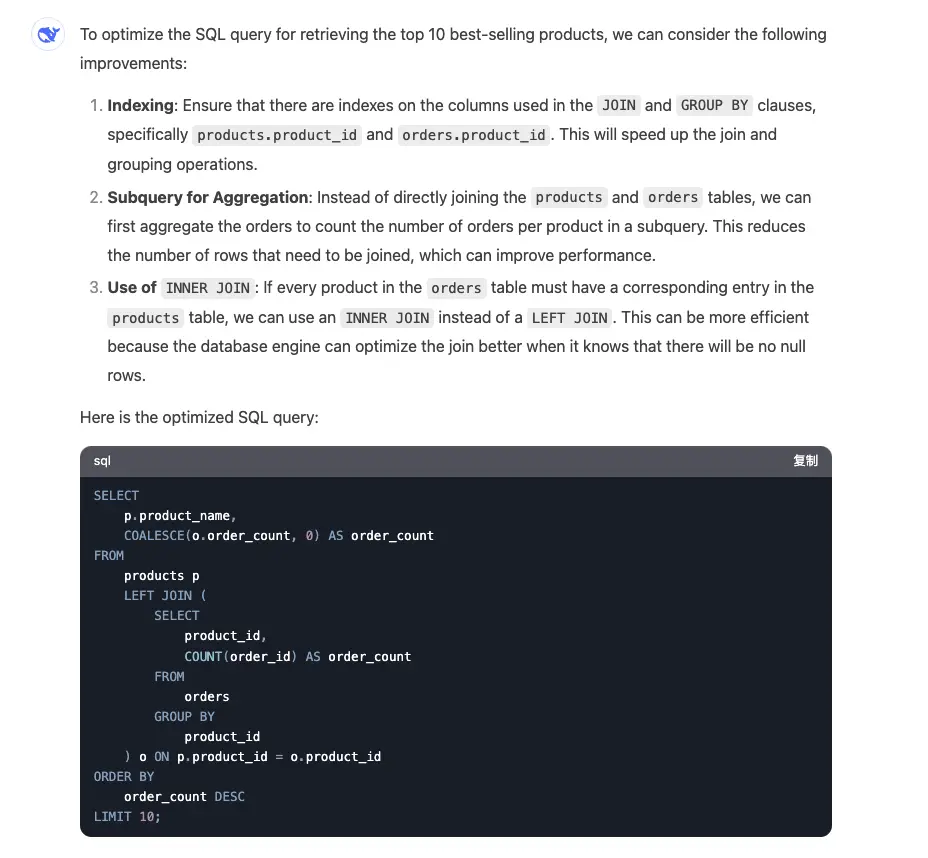
The AI accurately understands the relationship between product and order tables, judges table sizes, and field contents to generate optimal optimization suggestions, potentially even suggesting business-level transformations.
AI SQL optimization extends beyond SQL statements to business logic transformation. For example:
| |
Using AI for optimization:
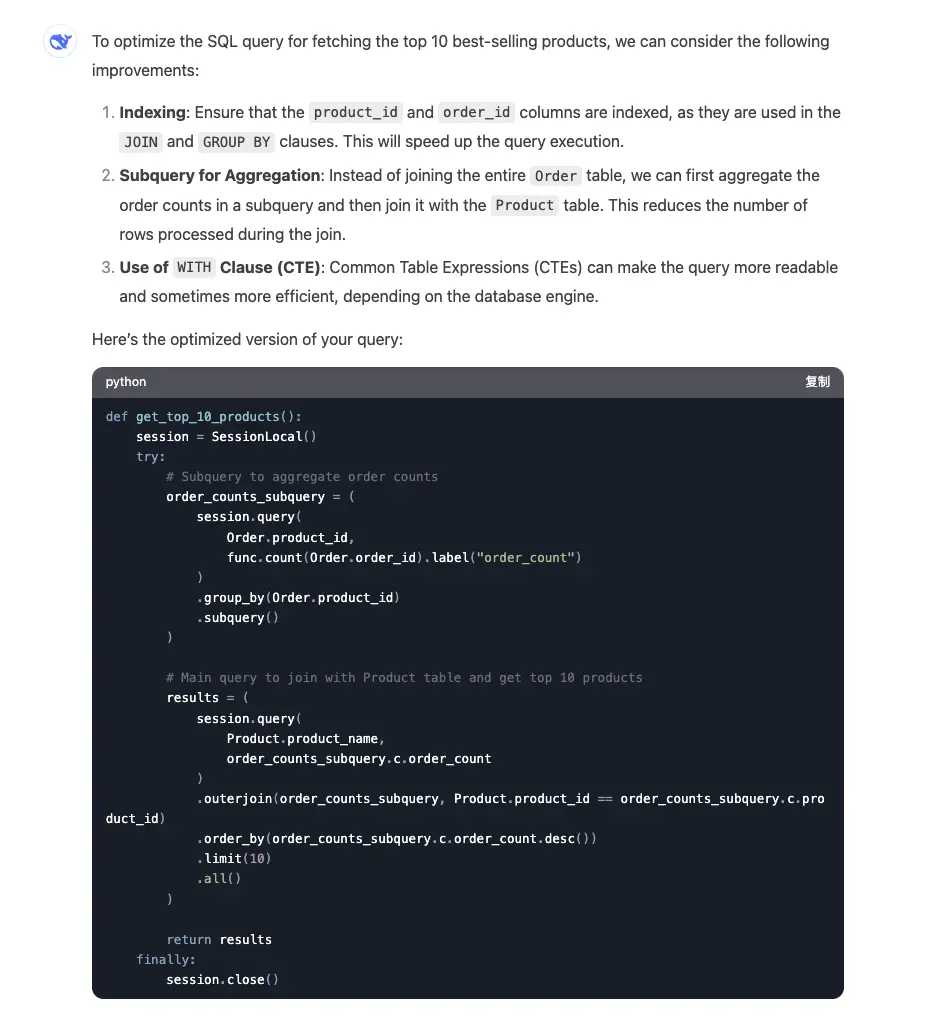
AI can directly analyze and optimize business logic, suggesting improvements without converting business code to SQL.
AI’s significant advantage in SQL optimization is generating specific rewrite suggestions rather than just diagnosing problems. For example:
| |
Traditional optimizer:
AI optimizer:
| Comparison Item | Traditional Optimizer | AI Optimizer |
|---|---|---|
| Problem Diagnosis | Identifies technical issues (e.g., nested subqueries, missing indexes) | Identifies technical issues and explains causes in business context |
| Rewrite Suggestions | Provides technical rewrite suggestions (e.g., create indexes) | Offers specific SQL rewrite plans and explains optimization logic |
| Business Understanding | Lacks business context, struggles to understand optimization significance | Contextualizes optimization steps within business scenarios |
| Developer Experience | Developers must independently comprehend optimization logic | Developers can quickly grasp optimization suggestions, reducing learning curve |
As AI and large model technologies mature, AI SQL optimization may evolve in several directions:
AI will function as a “virtual DBA,” engaging in a multi-round optimization process: diagnosing problems, proposing optimization suggestions, and validating optimization effects. If results are unsatisfactory, AI will automatically adjust strategies for further optimization until the optimal solution is achieved.
AI SQL optimization represents a revolution in the database field, significantly improving database performance and efficiency. Embrace AI to open a new chapter in SQL optimization!
SQLFlash is your AI-powered SQL Optimization Partner.
Based on AI models, we accurately identify SQL performance bottlenecks and optimize query performance, freeing you from the cumbersome SQL tuning process so you can fully focus on developing and implementing business logic.
Join us and experience the power of SQLFlash today!.